XLM
The XLM cross-lingual language model was described in the paper “Cross-lingual Language Model Pretraining”, published by Facebook in Janurary 2019.
Translation Language Modeling (TLM) Training Objective
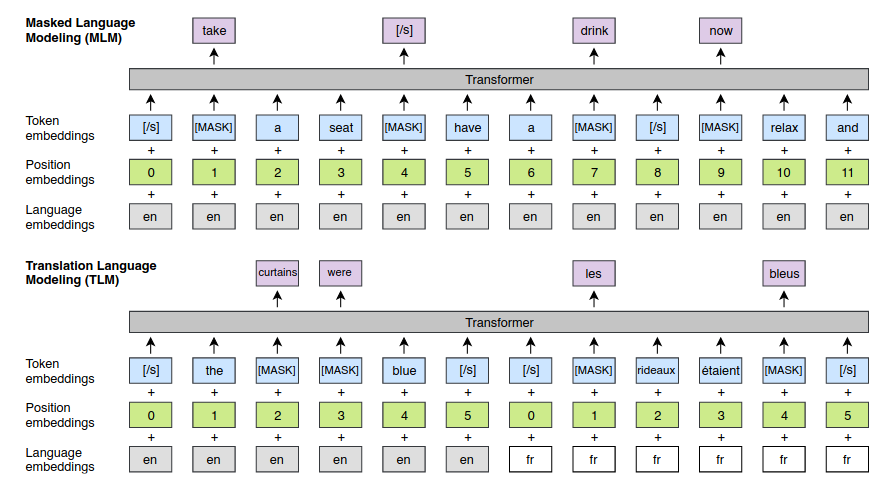
In addition to the masked language modeling (MLM) pretraining objective, the authors also investigated a translation language modeling (TLM) objective, illustrated in the following Figure (extracted from the paper). In TLM, parallel sentences are concatenated and masks are applied in both sentences. To predict a masked token, the model can attend to the sentence containing the mask, or to the parallel sentence, or both. This encourages the model to align token representations across languages. The positions of the target sentences are also reset.
Final Model
In their experiments, the authors found that using both MLM+TLM performs better than just using MLM. When TLM is used in combination with MLM, the model alternates between these two objectives. When using TLM, the batches contain parallel sentences instead of consecutive sentences (as in MLM).
Finally, all languages were subword tokenized with a shared Byte Pair Encoding (BPE) vocabulary. The BPE splits were learned on sentences sampled randomly from monolingual corpora.
