Tk-INSTRUCT - Encoder-Decoder fine-tuned on 1600+ NLP tasks
The Tk-INSTRUCT encoder-decoder language model is based on T5 11B, and is fine-tuned on a large dataset of 1,616 diverse NLP tasks with written instructions. It is described in the paper “Super-NaturalInstructions: Generalization via Declarative Instructions on 1600+ NLP Tasks”, published in April 2022. In the paper, the authors also built a multi-lingual version of their model, mTk-INSTRUCT, and shows that their proposed models outperform InstructGPT on their dataset.
Dataset
The authors collated a dataset Super-Natural-Instructions (Sup-NatInst) that consists of 1,616 NLP tasks with natural language instructions. The dataset is collected through community effort on GitHub.
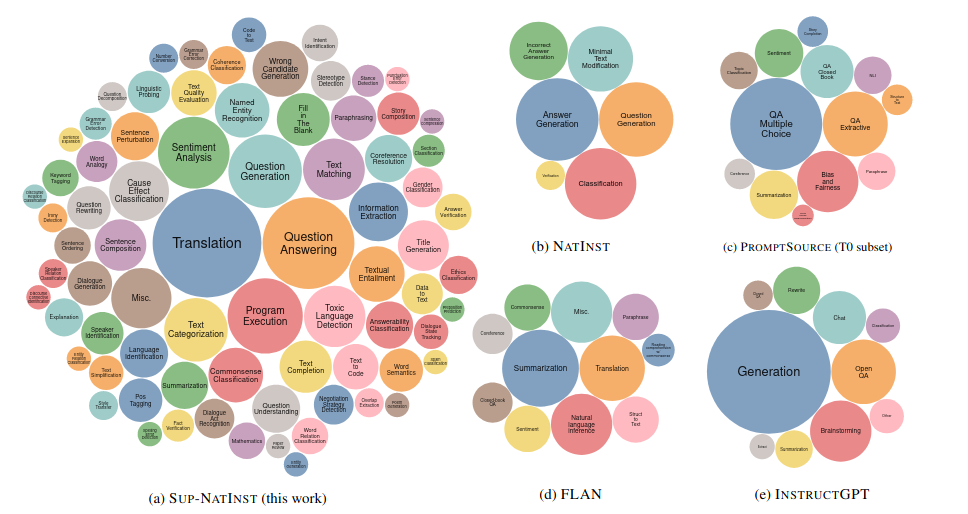
Each task can be defined by 3 dimensions: (i) task type: e.g. QA, classification, etc., (ii) language, (iii) domain, e.g. politics, medicine, dialogue, etc. In total, the dataset consists of 5M instances. Following is a Figure from the paper, illustrating the diverse range of tasks in Sup-NatInst, as compared to other existing datasets in the literature (bubble size represents the number of tasks of each type):
Following are some statistics on the dataset:
- 5M instances in total.
- Each instance consists of an instruction or task definiton (56.6 words long), and has an average of 2.8 positive examples and 2.4 negative examples.
- 1616 tasks of which 576 are non-English. Remember that each task is a combination of: task type, language, domain.
- 76 task types in 55 languages, and 33 domains.
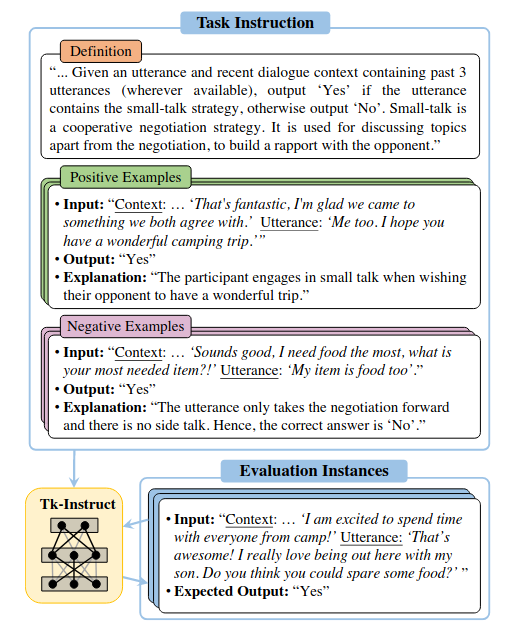
- an average of 3106 instances per task. Following is a Figure from the paper, illustrating a task. The model is expected to use the provided instructions (task definition and demonstration examples) to predict the responses.
The following Figure illustrates a prompt template for the model:

Tk-INSTRUCT model
After dividing the Sup-NatInst dataset into a training set and an evaluation set, the authors built two models:
- a monolingual English Tk-INSTRUCT by performing multi-task training of the T5 11B model using the training data of the Sup-NatInst dataset
- a multilingual variant mTk-INSTRUCT based on the mT5 13B model.
During inference, the models are given a task instance which consists of the instructions or task definition, and demonstration examples, and asked to predict the responses. ROUGE-L was used as the evaluation metric.
Evaluation
The authors compared against:
- pretrained language models: (i) T5-LM 11B which is T5 further trained with a lanuage modeling objective, (ii) GPT-3 175B.
- instruction-tuned models: (i) InstructGPT which uses reinforcement learning to incorporate human preferences into GPT-3, (ii) T0 which finetunes T5 on a collection of task prompts in the PROMPT-SOURCE dataset.
The experiments show that Tk-INSTRUCT (62.0 ROUGUE-L) performs better than InstructGPT 175B (52.1), and mTk-INSTRUCT (66.1) performs better than InstructGPT (52.8).
Cavets
While it is unclear whether InstructGPT’s training data overlaps with the evaluation data of this corpus, but at the same time, the style of prompting in InstructGPT’s training data might be very different from the prompting style in Sup-NatInst dataset.
The authors also made the following observations:
- Fine-tuning Tk-INSTRUCT on more tasks improves generalization performance. For each task, Sup-NatInst provides a single instruction, hence there are 1,616 different instructions. Contrast this with the 14,378 instructions that InstructGPT used.
- A large number of training instances do not help generalization. Tk-INSTRUCT models’ performance saturates with only 64 training instances per task. The authors had collected an average of 3106 instances per task, so most of these instances are not useful.
Hence, while this paper shows that Tk-INSTRUCT performs better than InstructGPT on the dataset that Tk-INSTRUCT was fine-tuned on, the cavet is that the prompts that InstructGPT was trained on might have a very different style thus leading to its lower performance. Also, the authors found that fine-tuning on very diverse tasks/instructions with only a few, e.g. 64, training instances per task, seem to be the optimal approach towards training a highly generalizable language model. This seems to coincide well with the approach that InstructGPT is taking, and is especially important when building a dialog model where the user prompts are inherently very diverse.
