T0 - Fine-Tuned Encoder-Decoder Language Model
The T0 model was introduced in the paper “Multitask Prompted Training Enables Zero-Shot Task Generalization” published in October 2021. The setup of T0 is very similar to the FLAN model from Google (published one month earlier in September 2021). The main difference being that T0 is based off the T5 model (encoder-decoder), while FLAN is based off LaMDA-PT (Google’s decoder-only language model).
The T0 paper shows that multitask prompted fine-tuning improves zero-shot performance on unseen tasks.
- T0 (11B parameters) also performs better than GPT-3 (175B parameters) on 9 out of 11 evaluation datasets, despite being 16x smaller in size.
- Note that GPT-3 is not fine-tuned on NLP datasets whereas T0 is. Neverthess, T0 is significantly smaller than GPT-3, thus allowing for more efficient deployment and follow-on fine-tuning
- The Figure below (extracted from the T0 paper) shows the approach in this paper: multi-task fine-tuning, then zero-shot evaluation.
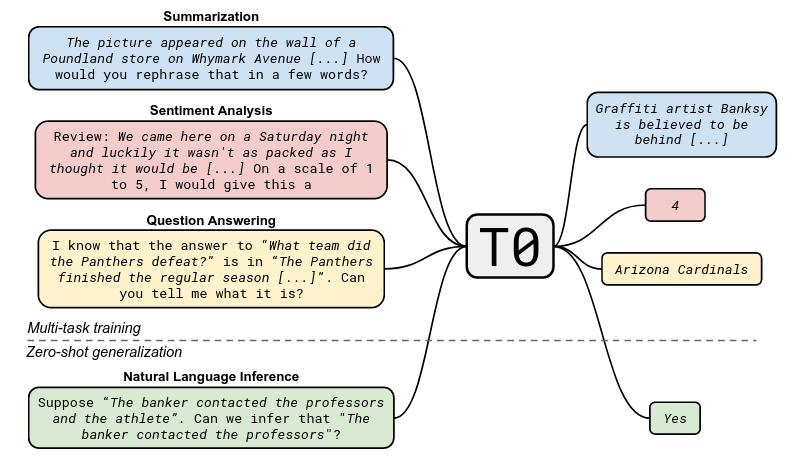
Other important takeaways from the paper are:
- FLAN finds that multitask fine-tuning on smaller models decreased performance. However, T0 finds that multitask fine-tuning improves performance on a model as small as 3B parameters. A likely reason is that FLAN is decoder-only, while T0 is encoder-decoder. Both the BERT and T5 papers had shown that MLM is a more effective pretraining objective vs autoregressive language modeling.
- Shows that training on a wider range of prompts per dataset improves the median and decreases the variability of performance on held-out tasks.
Model Training Details
- Starting from the T5 model (encoder-decoder pretrained with a span masked objective on 1T tokens from C4 dataset), continue pre-training as a standard language model, then perform multitask fine-tuning. Then evaluate on tasks the model was not finetuned on.
- All models are based off T5. But because T5’s pretraining objective is generating only tokens that have been removed from the input text, it is different from the natural text generation format of prompted datasets. Therefore, they used the T5+LM, which was produced by training T5 on 100B additional tokens from C4 on a standard language modeling objective.
- The T0 datasets and tasks are shown in the following Figure, extracted from the T0 paper. Train on Yellow, test on Green:
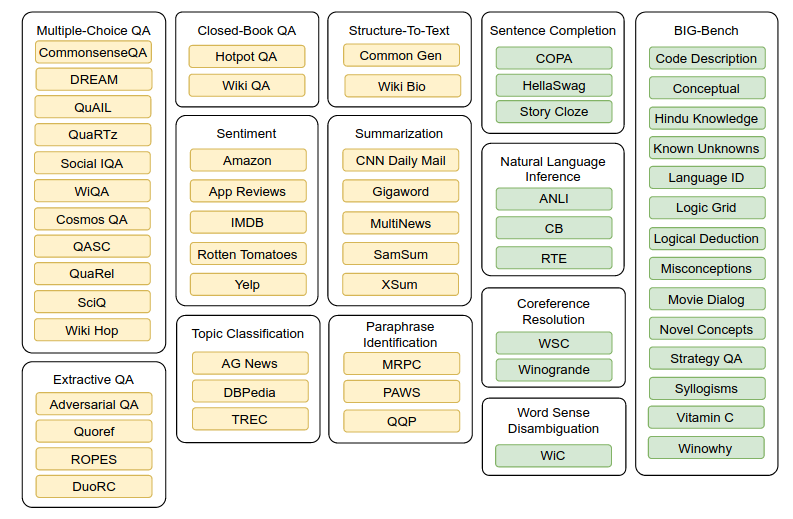
Training and evaluation:
- They choose the checkpoint that gives the highest score on the validation splits of the training datasets. This is still true zero-shot, as they do not use examples from any of the held-out tasks to select the best checkpoint.
- For tasks that choose the correct completion from several options (e.g. multiple choice QA), they use rank classification: compute the log-likelihood of each of the target options using the finetuned model, then select the option with the highest log-likelihood as the prediction. They did not apply length normalization to the log-likelihood on the target options.
Written on February 3, 2023
