MTEB Benchmark Dataset to Evaluate Sentence Embedding Models
The MTEB dataset primarily aims to evaluate (33) models’ ability to embed sentences or paragraphs. MTEB includes 8 different tasks over 56 datasets (of which 10 are multilingual), covering 112 different languages. Both sentence-level and paragraph-level data are included. The MTEB dataset was introduced in the paper “MTEB: Massive Text Embedding Benchmark”, published in October 2022.
Tasks and Datasets
The Figure below gives an overview of the tasks and datasets in MTEB. Purple shades indicate multilingual datasets. A brief description of the 8 different types follow. We can see that the datasets can be grouped into calculating similarities between three categories of text pairs: sentence-sentence, paragraph-paragraph, sentence-paragraph. Hence, MTEB evaluate models’ ability to embed sentences and paragraphs into effective representations:
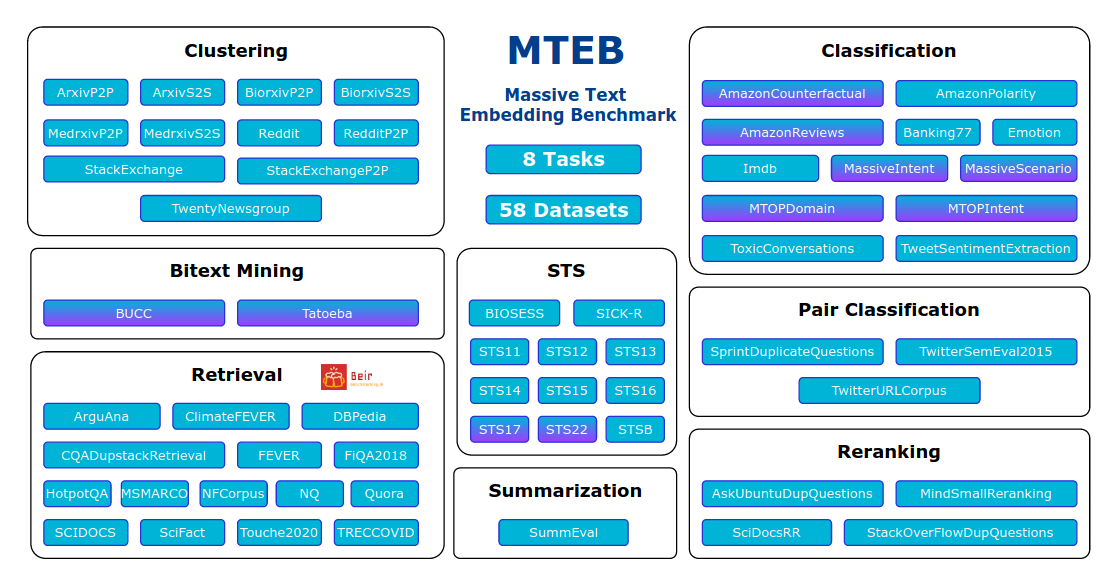
- Bitext mining: Given two sets of sentences (from two different languages). For each sentence in the first set, find the best matching sentence in the second set. The matches are commonly translations.
- Classification: Example classification tasks here are IMBD sentiment, intent classification, toxicity, Amazon review sentiment, etc. The authors cast this as a pairwise classification task by using the provided model to embed the training and test examples, which is then used to train a kNN-classifier.
- Clustering: Use the provided model to embed sentences and paragraphs, then a K-means model is applied to perform clustering.
- Pair classification: Given a pair of text inputs, predict the binary label, e.g. duplicate or paraphrase, etc. The texts are embedded with the provided model and pairwise distance is computed, e.g. using cosine similarity. Using the best binary threshold, precision is then calculated.
- Reranking: Given a query and a list of references (consisting of both relevant and irrelevant) texts. The model is used to embed the query and references, which are then compared to the query using cosine similarity to rerank the references. Metrics are mean MRR and MAP.
- Retrieval: Each given query has a list of relevant documents from a given corpus. The goal is to find these relevant documents. To provided model is used to embed queries and documents. Similarity scores are then calculated using cosine similarity. Metrics are nDCG, MRR, and MAP.
- Semantic textual similarity: Given a sentence pair, the task is to determine their similarity. Labels are continuous scores. Spearman correlation based on cosine similarity is the main metric.
- Summarization: Given a machine generated summary, the aim is calculate distances to all human generated summaries. The highest cosine similarity score is used as the model’s score of the machine summary.
Evaluation
The main results of the evaluation are as follows:
- The best models are ST5-XXL (11B, average score=59.51), GTR-XXL (11B, score=58.97), and SGPT-5.8B (score=58.81). ST5 is based on the encoder stack of the T5 model and fine-tuned with contrastive learning. SGPT is based on GPT-style decoder models and fine-tuned with contrastive learning.
- However, the above models are big in size and consume a lot of inference time. Taking both performance and speed into consideration, one should consider MPNet sentence embedding model (110M, score=57.78) and MiniLM sentence embedding model (96M, score=56.53).
- For multilingual data, the best model in terms of both performance and speed is MPNet-multilingual
