TransferTransfo Dialog Model
The TransferTransfo generative model is a dialog system (chatbot) from Huggingface, described in the paper “TransferTransfo: A Transfer Learning Approach for Neural Network Based Conversational Agents”, published in 2019.
Model Training
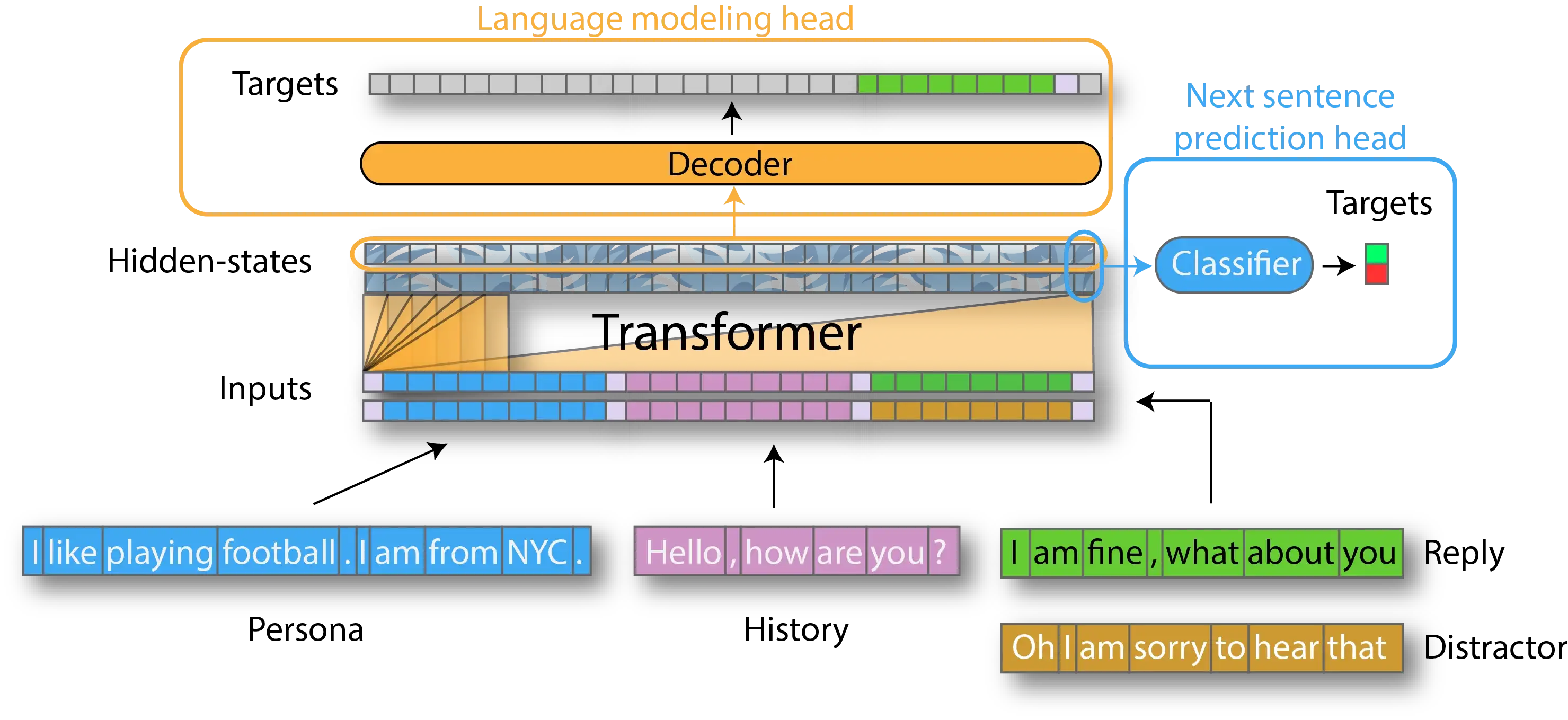
The authors leveraged the GPT generative model to build a coversation agent where they fine-tuned on the PERSONA-CHAT dataset (10K dialogs). When training, they optimize a combination of two losses: a next-utternace classification loss and a language modeling loss. In the PERSONA-CHAT dataset, there are a set of predefined “persona” which pre-conditions the dialog contents.
Each dialog example is a concatenation of:
- All the persona sentences of the current speaker (usually 4-6 sentences in the PERSONA-chat database).
- History of the dialog’s previous utterances (usually 3-5 previous utterances).
- The target utterance to generate.
Next utterance classification loss
- To form training samples, a correct next utterance (positive sample), and a set of 2-6 randomly sampled distractor utterances (negative samples) are collected. Each of these utterances are then individually appended to a given input sequence (the dialog thus far) to form a set of training samples.
- Given a training sample, a special token
[CLS]is appended to the end of the sample sequence. The last hidden state of this token (as given by the Transformer network) is then passed to a linear layer to compute classification probabilities. The parameters of the Transformer and linear classification layer are jointly fine-tuned to optimize the log probability of the correct label.
Language modeling loss
- This is the commonly used cross-entropy loss, where the final hidden states of the self-attention model is fed to softmax over the vocabulary, to obtain next token probabilities. These probabilities are then scored using a negative log-likelihood loss where the gold next tokens are taken as labels.
- Note that during fine-tuning, the language modeling loss is calculated only over the target utterance.
Model Details:
- The authors used the GPT model: 12-layer decoder only transformer with masked self-attention heads (768 dimension, 12 attention heads).
- Using pre-trained model weights open-sourced by OpenAI, the Huggingface team built an in-house implementation of GPT-1.
- Uses (pre-training) learned positional embeddings. Sequence length 512 tokens. Bytepair encoding (BPE) with 40K merges.
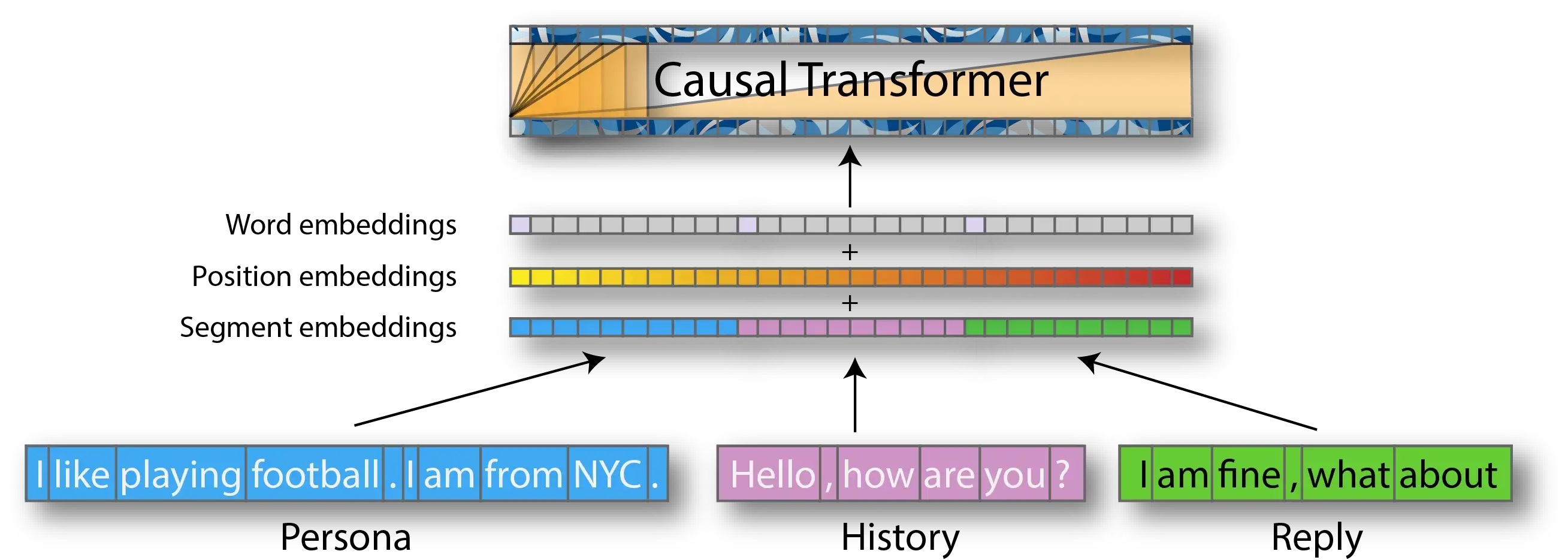
- Similar to the segment embeddings from BERT, the authors used “dialog state embeddings” to indicate whether the current token is part of (i) a personality sentence, (ii) an utterance from PERSON1, (iii) an utterance from PERSON2. These additional embeddings are also learned by fine-tuning on the PERSONAL-chat database.
- So each input token representation is a sum of 3 kinds of embeddings: (i) pre-trained word embeddings, (ii) pre-trained position embeddings, (iii) fine-tuned learnt “dialog state embeddings”.
The Figure below (extracted from the paper) illustrates the fine-tuning setup of the model. The model is tuned to optimize the losses from the languages modeling head (focusing loss on the reply), and the next sentence prediction head. Each input reply to predict is conditioned on the persona and chat history: