Holistic Evaluation of Language Models
The paper “Holistic Evaluation of Language Models” from Stanford, published in November 2022, is a large scale evaluation of 30 language models over a set of 16 scenarios and 7 categories of metrics.
Scenarios
The scenarios are what we want the models to do. These are triples of (task, domain, language):
- Task: what we want the model to do. QA, summarization, sentiment analysis, IR, toxicity detection.
- Domain: the type of data, properties of the text (what genre, who or which demographic group, when). Examples of what: Wikipedia, movie review, product review, news, twitter, reddit.
- Language: English
Examples are (QA, (clinical notes, doctors, now), English), (toxicity detection, (tweets, Egypt, Internet-era), Arabic).
Metrics
The metrics evaluated are the following:
- Accuracy: exact match, F1, MRR and NDCG in IR, ROUGE, etc.
- Calibration: a model is calibrated if it assigns meaningful probabilities to its predictions. If a well calibrated model predicts that 1,000 sentences are toxic each with probability 0.7, then we expect around 700 of them to be toxic.
- Robustness: Invariance measures how stable the model’s predictions are under small, semantics preserving perturbations (e.g. typos, capitalizations). Equivalence test whether a model is sensitive to perturbations that change the target output.
- Fairness: replace (race, gender) terms in test examples to see whether the model’s predictions stay the same.
- Bias: this counts the occurrences of gender and racial terms in the model’s generation, e.g. “The father, son, and daughter played soccer together.”, “male nurse”, “female nurse”.
- Toxicity: this tests for hate speech, violent speech, and abusive language. The paper used the Perspective API (Lees et al. 2022) to detect toxic content in model generations.
- Efficiency: evaluates training and inference efficiency.
Evaluation Setting
The following are the datasets used for evaluating the different scenario categories:
- Question answering: BoolQ, NewsQA, NarrativeQA, NaturalQuestions, QuAC, HellaSwag, OpenBookQA, TruthfulQA, MMLU
- Information retrieval: MS-MARCO
- Summarization: CNN/DailyMail, XSUM
- Sentiment analysis: IMDB
- Toxicity detection: CivilComments
- Text classification: RAFT
To evaluate the models, the authors used 5-shot prompting (i.e. there is no fine-tuning). The same 5-shot prompts are used for all models. The paper did not employ sophisticated prompting such as chain-of-thought. The following shows an example of a prompt:
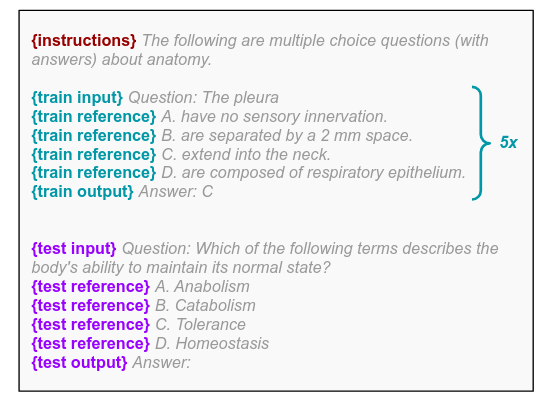
Models
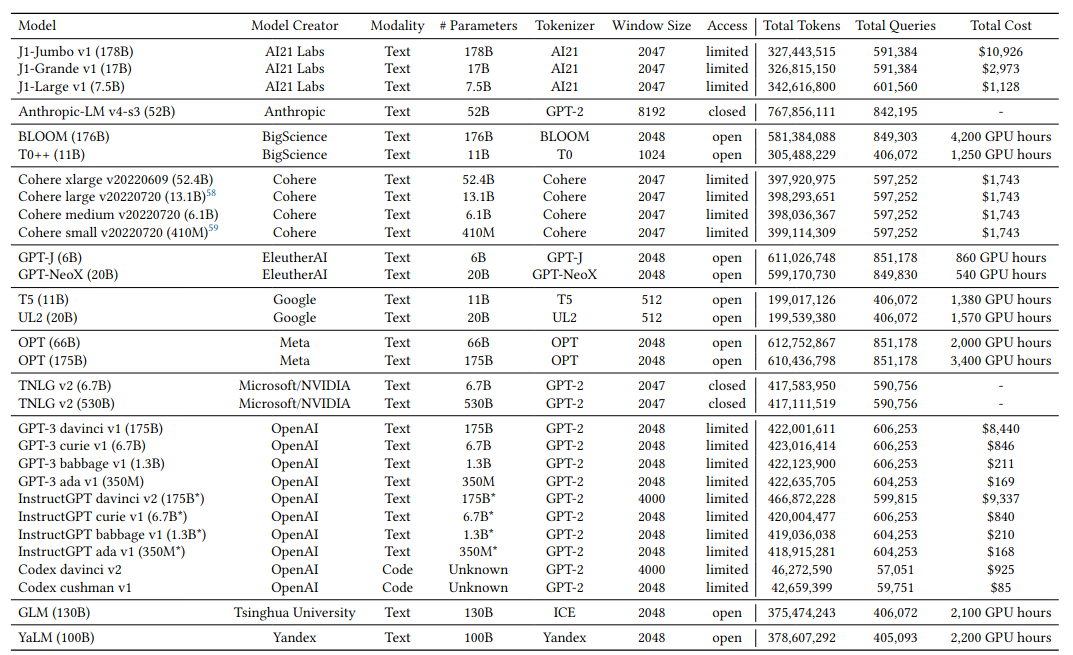
The 30 models evaluated are shown in the Table below. The total tokens, queries, and cost refer to the overall costs the paper authors incurred to evaluate the given model. The number of parameters for InstructGPT are estimates (hence the asterisk in the Table).
A brief description of the models are as follows:
- J1 (AI21 Labs): These are the Jurassic-1 autoregressive models ranging from 7.5B to 178B.
- Anthropic-LM (Anthropic): These are autoregressive models further trained on preferences and then fine-tuned with reinforcement learning on human feedback.
- BLOOM (BigScience): This is a multilingual autoregressive model trained on a corpus of 46 natural languages and 13 programming languages.
- T0++ (BigScience): This is an encoder-decoder model that is fine-tuned from T5 (11B) on a mixture of 55 datasets.
- Cohere (Cohere): These models are trained on undisclosed data in an undisclosed fashion.
- GPT-J (EleuhterAI): An autoregressive model trained on 400B tokens.
- GPT-NeoX (EleutherAI): An autoregressive model.
- T5 (Google): An encoder-decoder model trained on the C4 corpus (a filtered version of CommonCrawl).
- UL2 (Google): An encoder-decoder (same architecture as T5) that is also trained on the C4 corpus, using Mixture-of-Denoisers training objective.
- OPT (Meta): A family of autoregressive models, trained on the Pile, training data for RoBERTa, and corpus based on Reddit.
- TNLG-v2 (Microsoft/NVIDIA): A family of autoregressive models trained on a subset of the Pile and CommonCrawl.
- GPT-3 (OpenAI): A family of autoregressive models trained on 570GB of Internet text.
- InstructGPT (OpenAI): InstructGPT models are GPT-3 models fine-tuned with reinforcement learning on human feedback. However, based on https://twitter.com/janleike/status/1584618242756132864, the deployed model/API which OpenAI made available for use are not the exact InstructGPT models. Thus the model sizes and other settings for the InstructGPT models in the above table in the Evaluation Setting Section are estimates.
- Codex (OpenAI): These are GPT-3 models fine-tuned on source code from 54 million GitHub repositories. But similarly, the deployed model/API which OpenAI made available for use may not be the exact model setup publicly reported.
- GLM (Tsinghua University): A bidirectional model trained on English, Chinese, and multi-task data.
- YaLM (Yandex): An autoregressive model trained on 1.7TB of undisclosed data in English and Russian.
Evaluation Results
Head to head win rate of each model vs all other models are given below.
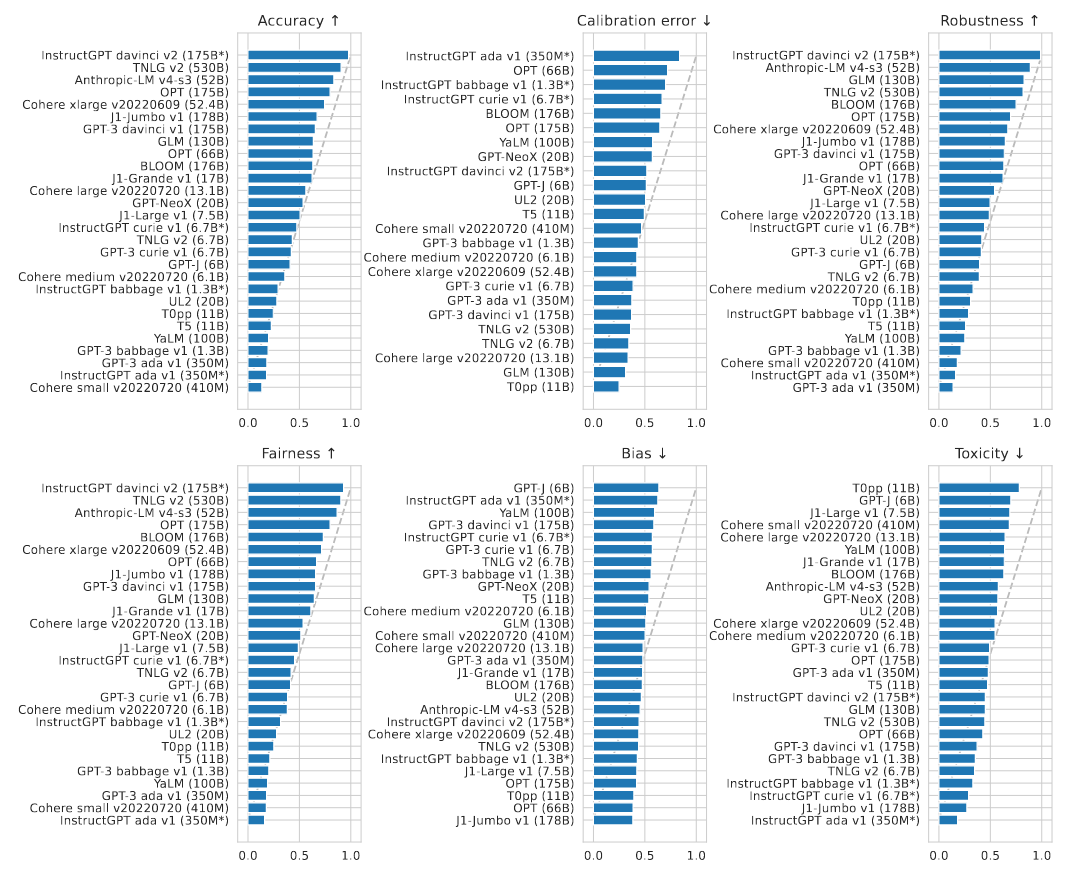
- In general, InstructGPT davinci-v2-175B performs best on accuracy, robustness, and fairness. TNLG v2-530B comes in second on accuracy and fairness. Anthropic-LM v4-s3-52B comes in top-3 for accuracy, robustness, and fairness.
- Memorization risk correlates with accuracy. In particular, (i) InstructGPT davinci-v2-175B, (ii) GPT-3 davinci-v1-175B, (iii) Antropic-LM v4-s3-52B, demonstrate the highest amount of verbatim regurgitation in line with their high accuracies.
- Within the same model family, model scale improves accuracy. All models that score well above chance (i.e. $>$ 55%) are at least 50B parameters.
The evaluation comes with important cavets though, as a few state-of-the-art language models are not included in the evaluation:
- Models that are instruction fine-tuned:
- FLAN-T5: a multi-task fine-tuned version of the T5 encoder-decoder model
- Tk-Instruct: a model based on T5, which is fine-tuned on the new Super-NaturalInstructions datasets and shown to out-perform InstructGPT.
- BLOOMZ: a fine-tuned version of the multilingual BLOOM model from BigScience workshop.
- Models without access:
- Gopher: 280B autoregressive model from DeepMind, trained on 300B tokens.
- Chinchilla: 70B autoregressive model trained on 1.4T tokens, shown to perform better than Gopher.
- LaMDA: Google’s 137B dialog autoregressive model
- PaLM: Google’s 540B autoregressive model, trained on 780B text tokens.
- FLAN-PaLM: Fine-tuned on the PaLM 540B autoregressive model, and is shown to perform better than PaLM.
