GPT-1 Decoder Language Model
The GPT-1 language model was introduced in the paper “Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training” in June 2018. The major contributions of GPT-1 are the following:
- Prior to GPT-1, it wasn’t clear or demonstrated that pre-training on Transformers would enable effective transfer learning to downstream tasks. The GPT-1 paper demonstrated that this approach of Transformer pre-training and fine-tuning works to produce SOTA results on various NLP tasks.
- They also showed that for fine-tuning downstream NLP tasks, instead of building task-specific model architectures, it is possible to perform task-specific input transformations and then generically stack on a linear classification layer on top of the pre-trained transformer.
To leverage the Transformer architecture, the authors could choose from various approaches: (i) encoder-only, (ii) decoder-only, (iii) encoder-decoder. They decide to use the decoder-only approach.
First, they performed unsupervised pre-training (using a language modeling objective of predicting the next word given previous contexts) on unlabeled texts. Then, they performed fine-tuning on downstream NLP tasks.
Unsupervised pre-training
Given a corpus of tokens $U = {u_1, \ldots, u_n}$, maximize the language modeling objective: \(L(U) = \sum_{i} \text{log } P(u_i | u_{i-k}, \ldots, u_{i-1}; \theta)\) Where $k$ is the window size, and $L(U)$ denotes likelihood of $U$.
GPT-1 used an autoregressive Transformer decoder for the language model, followed by feedforward layers to produce an output distribution over target tokens: * $h_0 = C W_e + W_p$ * $h_l = \text{transformer-block}(h_{l-1}) \forall_l \in [1,n]$ * $P(u) = \text{softmax}(h_n W_{e}^{T})$
In the above, $C = (u_{-k}, \ldots, u_{-1})$ is the context vector of tokens, $W_e$ is the token embedding matrix, and $W_p$ is the position embedding matrix. After the token embeddings are aggregated with the position embeddings to represent the input tokens, they are processed through multiple layers of Transformer blocks.
After producing the final hidden representation $h_n$ at layer $n$, we dot-product against the token embedding matrix $W_e$ to produce logits for every word in the vocabulary, and then take softmax to produce prediction probabilities of the predicted next word.
Model pre-training details
- GPT-1 was pre-trained on the BooksCorpus dataset, which is a collection of 7,000 unique unpublished books from a variety of genres (Adventure, Fantasy, and Romance, etc.) totalling about 1 billion words.
- The model includes a 12 layer decoder-only transformer with masked self attention heads (768 dimensionality, 12 attention heads). For the feed-forward networks, GPT-1 used $768 * 4 = 3072$ dimensional hidden states.
- They trained for 100 epoches on minibatches of 64 samples, using sequence length of 512 tokens. Tokenization is performed with Byte Pair Encoding (BPE).
- Weight initialization follows $N(0, 0.02)$. Residual, embedding, and attention dropouts at 0.1 rate for regularization.
- Used the Gaussian Error Linear Unit (GELU) as the activation function, and use learned position embeddings.
Supervised fine-tuning
Given a labeled dataset $D$ where each example consists of a sequence of input tokens $x^{1}, \ldots, x^{m}$ along with a label $y$, they maximize the objective: \(L(D) = \sum_{(x,y)} \text{log} P(y|x^{1}, \ldots, x^{m})\)
-
Where $P(y|x^{1}, \ldots, x^{m}) = \text{softmax}(h_{l}^{m} W_y)$. The inputs are passed through the pre-trained model to obtain $h_{l}^{m}$ (hidden representation of last token $x^{m}$ at final transformer block $l$), which is fed into a linear classification layer $W_y$ to obtain logits, then softmax to obtain classification prediction. We show below a Figure from the GPT-1 paper, illustrating the fine-tuning setup.
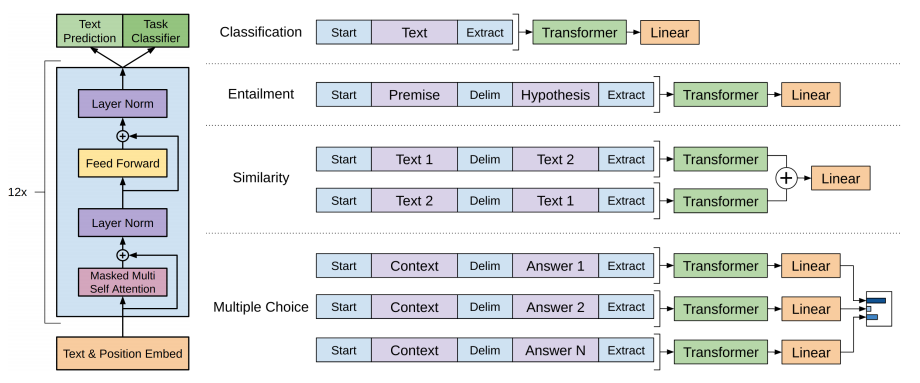
- All text inputs are concatenated with special delimiters: start token $\langle s \rangle$, extract token $\langle e \rangle$, delimiter token $($)$. These are represented as embedding vectors that are randomly initialized.
- For multiple choice question answering (QA) tasks where each example consists of a document $z$, question $q$, and a set of $N$ possible answers ${ a_k }$, they form $N$ individual text sequences: $[z; q; $; a_k]$. Each of these sequences are passed through the pre-trained transformer model and then a linear classification layer to obtain logits, then normalized via softmax for predictions.
Fine-Tuning Evaluation
- The GPT-1 paper evaluated on a variety of NLP datasets such as natural language inference (NLI a.k.a entailment), QA, GLUE, sentence similarity, sentiment, sentence linguistic acceptability, etc. and achieved SOTA results in 9 out of 12 datasets.
- They also designed some heuristics to probe the zero-shot inference capability of their model (e.g. for sentiment, append the token very to each example and note the model’s output logit scores for the words positive and negative).
