GLaM - MoE Decoder Language Model
The GLaM model (Generalist Language Models) was described in the paper “GLaM: Efficient Scaling of Language Models with Mixture-of-Experts”, published in December 2021. It is a decoder-only language model that does conditional computation using mixture of experts (MoE).
The largest GLaM model is 1.2T parameters with 64 experts (64E) per MoE (mixture of experts) layer. Each token in the input batch only activates a subset of 96.6B (8% of 1.2T) parameters.
It is more efficient than GPT-3 in training and inference, while better than GPT-3 in zero-shot, one-shot, and few-shot learning on 29 NLP tasks.
- Using their 64B/64E GLaM model (96.6B activated parameters, so half of GPT-3), they are better than GPT-3 in zero-shot, one-shot and few-shot.
- However, their 8B/64E model is worse than GPT-3.
Model Architecture
The GLaM architecture is illustrated in the following Figure, extracted from the paper:
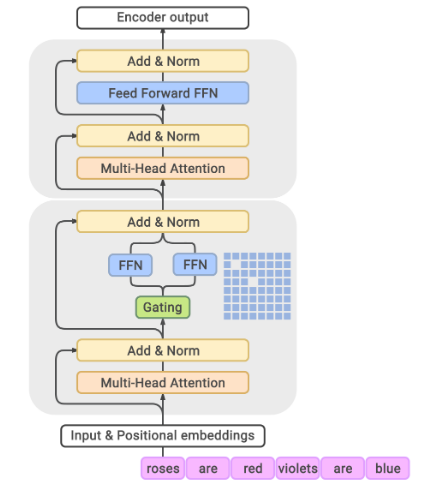
- Each MoE layer (the bottom block) is interleaved with a Transformer layer (the upper block). For each input token, the Gating module dynamically selects two most relevant experts out of 64. The weighted average of the outputs from these two experts will then be passed to the upper Transformer layer.
- Each MoE layer consists of a collection of independent feed-forward networks as ‘experts’. The gating function uses a softmax to model probability distribution over these experts (how well each expert is able to process the incoming input).
Written on February 17, 2023
