FLAN-PaLM - Fine-Tuned Decoder Language Model
The Flan-PaLM model was described in the paper “Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models” published in October 2022.
This paper presents very large scale instruction fine-tuning performed on T5 and PaLM models. Comparing instruction finetuned Flan-PaLM vs pretrained PaLM (of different sizes: 8B, 62B, 540B), multi-task instruction finetuning significantly improves performance compared to no finetuning.
In addition to the above, instead of using direct prompting during inference, adding chain-of-thought (CoT) prompts and self-consistency (SC) final answer selection further improves performance. Instruction finetuning on CoT data (both with and without examplars) enables performing CoT reasoning in a zero-shot inference setting.
This Flan-PaLM 540B CoT+SC is probably the current best decoder-only model. But it used the PaLM model, which is probably still under-trained (PaLM despite being 540B in size, was only trained on 780B tokens), hence should continue training on more text tokens.
Fine-Tuning Experiments
As fine-tuning NLP datasets, the authors used 473 datasets mined from prior work, across 146 task categories (e.g. commonsense reasoning, NER, conversational QA, closed-book QA, NLI, extractive QA, topic classification, etc.) and 1.8K tasks.
The authors experimented with various styles of finetuning prompts:
- With and without exemplars
- With and without CoT. Only 9 datasets come with CoT-style prompts.
- Some data formats are without instructions but just with few-shot examplars.
The Figure below (extracted from the paper) illustrates different styles of prompts. Left of arrow is given context. Right of arrow are meant to be predicted by the language model.
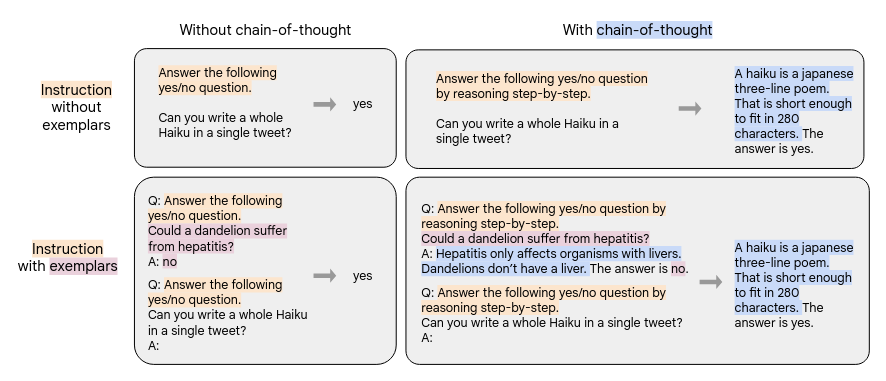
- Applied instruction finetuning to T5, PaLM, U-PaLM. Packed or combined multiple training examples into a single sequence (for space efficiency), separating inputs from targets using an end-of-sequence token. Masking is applied to prevent the tokens from attending to others across the packed example boundary.
Evaluation
- During evaluation, all test prompts contain few-shot examplars.
- Comparing instruction finetuned Flan-PaLM vs pretrained PaLM (of different sizes: 8B, 62B, 540B), multi-task instruction finetuning significantly improves performance compared to no finetuning.
- In addition to the above, instead of using direct prompting during inference, adding CoT prompts and self-consistency final answer selection further improves performance.
- However, the majority of the finetuning improvement comes from using up to 282 tasks. Thereafter the improvements starts to level off. Two potential explanations:
- (i) the additional tasks are not particularly diverse, so they are not providing the model with new knowledge.
- (ii) most of the gains from multi-task instruction finetuning come from the model learning to better express knowledge that it already knows from pretraining.
- The instruction fine-tuning dataset include 9 CoT datasets. Evaluation shows that mixing CoT and non-CoT datasets during fine-tuning improves test performance on CoT benchmarks (than just CoT finetuning alone), and does not compromise performance on non-CoT benchmarks (compared to finetuning on non-CoT only). I.e. mixing together both CoT and non-CoT data is beneficial towards improving model performance on all evaluation benchmarks.
- Instruction finetuning on CoT data (both with and without examplars) enables performing CoT reasoning in a zero-shot inference setting.
- The Instruct-GPT prior work mentioned that standard NLP automatic metrics are not sufficient to measure human preferences among open-form zero-shot responses from language models, and that finetuning with a set of labeler demonstrations (as well as reinforcement learning from human feedback) is important. Hence, the authors of Flan-PaLM also performed qualitative evaluation. In this work, the authors created an evaluation set of 190 questions (in categories: creativity, reasoning over contexts, complex reasoning, planning, explanation) posed in a zero-shot setting. Flan-PaLM generations were preferred over PaLM by humans 79% of the time.
